若有以下程序: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class data public: int x; data(int x) { data: :x=x; }; class A private: data d1; public: A(int x): d1(x){} void dispa() { cout<<d1.x<<","; } }; class B: public A { private: data d2; public: B(int x): A(x-1),d2(x){} void dispb() { cout<<d2.x<<end1; } }; class C: public B { public: C(int x): B(x-1){} void disp() { dispa(); dispb(); } }; int main() { C obj(5); obj.disp(); return 0; 程序执行后的输出结果是 }
A.5,5
B.4,5
C.3,4
D.4,3
第1题:
以下程序执行后的输出结果是 #include <iostream> using namespace std; void try(int,int,int,int); int main () { int x,y,z,r; x =1 ; y = 2; try(x,y,z,r); cout<<r<<endl; return 0; } void try(int x,int y,int z,int r) { z = x+y; x = x*x; y = y*y; r = z+x+y; }
A.18
B.9
C.10
D.不确定
第2题:
若有以下程序: #include<iostream> using namespace.std; class data { public: int x; data (int x) { data::x=x; } ); class A { private: data d1; public: A(int x) :dl(X){} void dispa() { cout<<dl.X<<","; } }; class B:public A { private: data d2; public: B(int x) : A(x-1),d2(x){} void dispb() { cout<<d2.x<<endl; } }; class C:public B { public: C(int x) :B(x-1){} void disp() { dispa(); dispb(); } }; int main() { C obj(5); obj.disp(); return 0; } 程序执行后的输出结果是
A.5,5
B.4,5
C.3,4
D.4,3
第3题:
若有以下程序段: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main () { int a[]={1,4,5}; int *p=&a[0],x=6, y,z; for (y=0; y<3; y++) z= ( (* (p+y) <x) ? *(p+y) :x); cout<<z<<end1; return 0; } 程序运行后的输出结果是( )。
A.1
B.4
C.5
D.2
第4题:
00330038003000301585067361821下列程序段执行结果是___________。 x = 1 print(type(x)) x = 1.0 print(type(x)) x = '1.0' print(type(x)
A.<class 'int'> <class 'float'> <class 'str'>
B.<class 'float'> <class 'int'> <class 'str'>
C.<class 'str'> <class 'float'> <class 'int'>
D.<class 'str'> <class 'int'> <class 'float'>
第5题:
以下程序执行后的输出结果是 #include<iostream>. using namespace std; void try(int,int,int,int); int main() { int x,y,z,r; x=1; y=2; try(x,y,z,r); cout<<r<<end1; return 0; } void try(int x,int y, int z,int r) { z = x+y; x = x*x; y = y*y; r = z+x+y; }
A.18
B.9
C.10
D.不确定
第6题:
以下程序执行后的输出结果是 #include<iostream> using namcspace std; void try(int,int,int,int); int main() { int x,y,z,r; x=1; y=2; try(x,y,z,r); cout<<r<<end1; return 0; } void try(int x,int y, int z,int r) { z = x+y; x = x*x; y = y*y; r = z+x+y; }
A.18
B.9
C.10
D.不确定
第7题:
以下程序执行后的输出结果是( )。 #include<iostream> using namespace std; void try(int,int,int,int); int main() { int x,y,z,r; x=1; y=2; try(x,y,z,r); cout<<r<<endl; return 0; } void try(int x,int y, int z,int r) { z = x+y; X = x*x; y = y*y; r = z+x+y; }
A.18
B.9
C.10
D.不确定
第8题:
以下程序执行后的输出结果是( )。 #include <iostream> using namespace std; void try(int,int,int,int); int main ( ) { int x,y,z,r; x=1; y=2; try(x,y,z,r); cout<<r<<end1; return 0; } void try(int x,int y, int z,int r) { z = x+y; x = X*X; y = y*y; r = z+x+y; }
A.18
B.9
C.10
D.不确定
第9题:
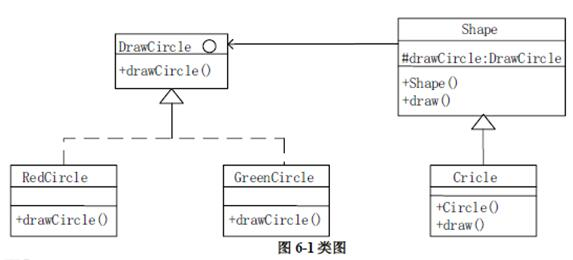
第10题:
下列程序段执行结果是___________。 x = 1 print(type(x)) x = 1.0 print(type(x)) x = '1.0' print(type(x)
A.<class 'int'> <class 'float'> <class 'str'>
B.<class 'float'> <class 'int'> <class 'str'>
C.<class 'str'> <class 'float'> <class 'int'>
D.<class 'str'> <class 'int'> <class 'float'>