(b) Explain how the process of developing scenarios might help John better understand the macro-environmental
factors influencing Airtite’s future strategy. (8 marks)
第1题:
5 All managers need to understand the importance of motivation in the workplace.
Required:
(a) Explain the ‘content theory’ of motivation. (5 marks)
第2题:
(c) Explain how Perfect Shopper might re-structure its downstream supply chain to address the problems
identified in the scenario. (10 marks)
第3题:
(ii) how effective delegation might be achieved; (6 marks)
第4题:
Matthew Black is well aware that the achievement of the growth targets for the 2005 to 2007 period will depend on
successful implementation of the strategy, affecting all parts of the company’s activities.
(c) Explain the key issues affecting implementation and the changes necessary to achieve Universal’s ambitious
growth strategy. (15 marks)
第5题:
3 Airtite was set up in 2000 as a low cost airline operating from a number of regional airports in Europe. Using these
less popular airports was a much cheaper alternative to the major city airports and supported Airtite’s low cost service,
modelled on existing low cost competitors. These providers had effectively transformed air travel in Europe and, in so
doing, contributed to an unparalleled expansion in airline travel by both business and leisure passengers. Airtite used
one type of aircraft, tightly controlled staffing levels and costs, relied entirely on online bookings and achieved high
levels of capacity utilisation and punctuality. Its route network had grown each year and included new routes to some
of the 15 countries that had joined the EU in 2004. Airtite’s founder and Chief Executive, John Sykes, was an
aggressive businessman ever willing to challenge governments and competitors wherever they impeded his airline and
looking to generate positive publicity whenever possible.
John is now looking to develop a strategy which will secure Airtite’s growth and development over the next 10 years.
He can see a number of environmental trends emerging which could significantly affect the success or otherwise of
any developed strategy. 2006 had seen fuel costs continue to rise reflecting the continuing uncertainty over global
fuel supplies. Fuel costs currently account for 25% of Airtite’s operating costs. Conversely, the improving efficiency of
aircraft engines and the next generation of larger aircraft are increasing the operating efficiency of newer aircraft and
reducing harmful emissions. Concern with fuel also extends to pollution effects on global warming and climate
change. Co-ordinated global action on aircraft emissions cannot be ruled out, either in the form. of higher taxes on
pollution or limits on the growth in air travel. On the positive side European governments are anxious to continue to
support increased competition in air travel and to encourage low cost operators competing against the over-staffed
and loss-making national flag carriers.
The signals for future passenger demand are also confused. Much of the increased demand for low cost air travel to
date has come from increased leisure travel by families and retired people. However families are predicted to become
smaller and the population increasingly aged. In addition there are concerns over the ability of countries to support
the increasing number of one-parent families with limited incomes and an ageing population dependent on state
pensions. There is a distinct possibility of the retirement age being increased and governments demanding a higher
level of personal contribution towards an individual’s retirement pension. Such a change will have a significant impact
on an individual’s disposable income and with people working longer reduce the numbers able to enjoy leisure travel.
Finally, air travel will continue to reflect global economic activity and associated economic booms and slumps together
with global political instability in the shape of wars, terrorism and natural disasters.
John is uncertain as to how to take account of these conflicting trends in the development of Airtite’s 10-year strategy
and has asked for your advice.
Required:
(a) Using models where appropriate, provide John with an environmental analysis of the conditions affecting the
low cost air travel industry. (12 marks)
第6题:
(b) Explain how Perfect Shopper might re-structure its upstream supply chain to address the problems identified
in the scenario. (10 marks)
第7题:
(b) Good Sports Limited has successfully followed a niche strategy to date.
Assess the extent to which an appropriate e-business strategy could help support such a niche strategy.
(8 marks)
第8题:
5 Your manager has heard of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory and how it has some relevance to motivational techniques.
Required:
(a) Explain Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. (10 marks)
5 The way in which managers’ duties are undertaken can significantly influence the satisfaction that employees derive from their work. Abraham Maslow suggested that individuals have a hierarchy of personal needs which are identifiable, universally applicable and can be satisfied in the workplace. Understanding this concept provides guidance to management as to the appropriateness of
motivational techniques.
(a) Maslow’s theory of motivation is a content theory. Its basic idea is that each individual has a set of needs which have to be
satisfied in a set order of priority.
Maslow suggested that individuals have five needs:
Self-actualisation
(or self fulfilment)
Esteem needs
(or ego)
Social needs
Safety needs
Physiological needs
These needs are arranged in a hierarchy of importance and movement is upwards, from physiological needs to selfactualisation.Any individual will always want more; each need must be satisfied before the next is sought. However – andcritically so far as motivation in the workplace is concerned – a satisfied need is no longer a motivator.
The theory is usually presented in the shape of a triangle, with physiological needs at its base and self-actualisation at itsapex. The triangle shape has a clear significance. As an individual moves up toward the apex, the needs thin out, that isphysiological needs are far greater than self-actualisation needs. For many individuals, reaching social needs is often thehighest need to be satisfied. The theory is sometimes presented as a staircase; again with self-actualisation at the top. Thissecond diagrammatic form. reflects the application of the theory to more modern situations, where it can reasonably beassumed that those within the organisation have already achieved physiological and safety needs. For such individuals, socialand esteem needs may well be greater.
Physiological needs are the basic survival needs which, although part of the theory, probably have less relevance today. Theseneeds are usually seen as food, shelter (which is sometimes noted as a safety need), warmth and clothing.
Safety needs are the desire for security, order, certainty and predictability in life and freedom from threat. The above two so-called ‘lower order needs’ dominate until satisfied.
Social needs are the gregarious needs of mankind, the need for friendship, relationships and affection. This is often seen as the desire to be part of a family.
Esteem needs are the desire for recognition and respect, often associated with status, especially in the modern world.
Self-actualisation (self fulfilment) is the ultimate goal. Once this state is achieved the individual has fulfilled personal potential.
However, later work by Maslow has suggested that there are two additional needs; freedom of enquiry (free speech and justice) and knowledge (the need to explore and learn). These additional needs are a further development of social needs and recognise the changing nature of modern life.
第9题:
(b) What advantages and disadvantages might result from outsourcing Global Imaging’s HR function?
(8 marks)
第10题:
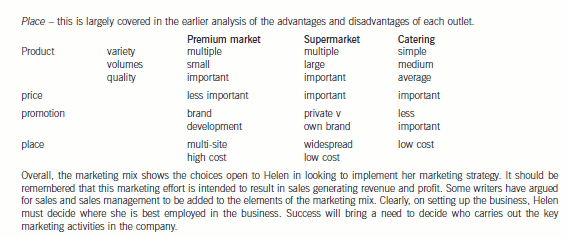
(b) How might the marketing mix vary between the three channels Helen is considering using? (8 marks)